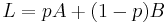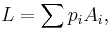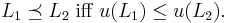Utility
| Part of a series on |
| Utilitarianism |
|---|
|
Predecessors
|
|
People
|
|
Key concepts
|
|
Problems
Mere addition paradox
Paradox of hedonism Utility monster |
|
Related topics
|
| Politics portal |
In economics, utility is a measure of relative satisfaction. Given this measure, one may speak meaningfully of increasing or decreasing utility, and thereby explain economic behavior in terms of attempts to increase one's utility. Utility is often modeled to be affected by consumption of various goods and services, possession of wealth and spending of leisure time.
The doctrine of utilitarianism saw the maximization of utility as a moral criterion for the organization of society. According to utilitarians, such as Jeremy Bentham (1748–1832) and John Stuart Mill (1806–1876), society should aim to maximize the total utility of individuals, aiming for "the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people". Another theory forwarded by John Rawls (1921–2002) would have society maximize the utility of the individual initially receiving the minimum amount of utility.
Utility is usually applied by economists in such constructs as the indifference curve, which plot the combination of commodities that an individual or a society would accept to maintain a given level of satisfaction. Individual utility and social utility can be construed as the dependent variable of a utility function (such as an indifference curve map) and a social welfare function respectively. When coupled with production or commodity constraints, under some assumptions, these functions can represent Pareto efficiency, such as illustrated by Edgeworth boxes in contract curves. Such efficiency is a central concept in welfare economics.
Contents |
Quantifying utility
It was recognized that utility could not be measured or observed directly, so instead economists devised a way to measure actual behavior and assume that, in a perfectly competitive equilibrium, this behavior reveals the underlying relative utilities. These 'revealed preferences', as they were named by Paul Samuelson, were revealed in price:
Utility is taken to be correlative to Desire or Want. It has been already argued that desires cannot be measured directly, but only indirectly, by the outward phenomena to which they give rise: and that in those cases with which economics is chiefly concerned the measure is found in the price which a person is willing to pay for the fulfilment or satisfaction of his desire. (Marshall 1920:78)[1]
Cardinal and ordinal utility
Economists distinguish between cardinal utility and ordinal utility. When cardinal utility is used, the magnitude of utility differences is treated as an ethically or behaviorally significant quantity. On the other hand, ordinal utility captures only ranking and not strength of preferences.
Utility functions of both sorts assign a ranking to members of a choice set. For example, suppose a cup of orange juice has utility of 120 utils, a cup of tea has a utility of 80 utils, and a cup of water has a utility of 40 utils. When speaking of cardinal utility, it could be concluded that the cup of orange juice is better than the cup of tea by exactly the same amount by which the cup of tea is better than the cup of water. One is not entitled to conclude, however, that the cup of tea is two thirds as good as the cup of juice, because this conclusion would depend not only on magnitudes of utility differences, but also on the "zero" of utility.
It is tempting when dealing with cardinal utility to aggregate utilities across persons. The argument against this is that interpersonal comparisons of utility are suspect because there is no good way to interpret how different people value consumption bundles.
When ordinal utilities are used, differences in utils are treated as ethically or behaviorally meaningless: the utility index encode a full behavioral ordering between members of a choice set, but tells nothing about the related strength of preferences. In the above example, it would only be possible to say that juice is preferred to tea to water, but no more.
Neoclassical economics has largely retreated from using cardinal utility functions as the basic objects of economic analysis, in favor of considering agent preferences over choice sets. However, preference relations can often be represented by utility functions satisfying several properties.
Ordinal utility functions are equivalent up to positive monotone transformations, while cardinal utilities are equivalent up to positive linear transformations.
Although preferences are the conventional foundation of microeconomics, it is often convenient to represent preferences with a utility function and analyze human behavior indirectly with utility functions. Let X be the consumption set, the set of all mutually-exclusive baskets the consumer could conceivably consume (such as an indifference curve map without the indifference curves). The consumer's utility function 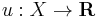 ranks each package in the consumption set. If the consumer strictly prefers x to y or is indifferent between them, then u(x) ≥ u(y).
ranks each package in the consumption set. If the consumer strictly prefers x to y or is indifferent between them, then u(x) ≥ u(y).
For example, suppose a consumer's consumption set is X = {nothing, 1 apple,1 orange, 1 apple and 1 orange, 2 apples, 2 oranges}, and its utility function is u(nothing) = 0, u(1 apple) = 1, u(1 orange) = 2, u(1 apple and 1 orange) = 4, u(2 apples) = 2 and u(2 oranges) = 3. Then this consumer prefers 1 orange to 1 apple, but prefers one of each to 2 oranges.
In microeconomic models, there are usually a finite set of L commodities, and a consumer may consume an arbitrary amount of each commodity. This gives a consumption set of 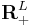 , and each package
, and each package 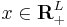 is a vector containing the amounts of each commodity. In the previous example, we might say there are two commodities: apples and oranges. If we say apples is the first commodity, and oranges the second, then the consumption set
is a vector containing the amounts of each commodity. In the previous example, we might say there are two commodities: apples and oranges. If we say apples is the first commodity, and oranges the second, then the consumption set 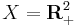 and u(0, 0) = 0, u(1, 0) = 1, u(0, 1) = 2, u(1, 1) = 4, u(2, 0) = 2, u(0, 2) = 3 as before. Note that for u to be a utility function on X, it must be defined for every package in X.
and u(0, 0) = 0, u(1, 0) = 1, u(0, 1) = 2, u(1, 1) = 4, u(2, 0) = 2, u(0, 2) = 3 as before. Note that for u to be a utility function on X, it must be defined for every package in X.
A utility function 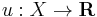 rationalizes a preference relation
rationalizes a preference relation 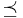 on X if for every
on X if for every 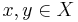 ,
, 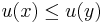 if and only if
if and only if 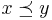 . If u rationalizes
. If u rationalizes 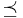 , then this implies
, then this implies 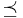 is complete and transitive, and hence rational.
is complete and transitive, and hence rational.
In order to simplify calculations, various assumptions have been made of utility functions.
- CES (constant elasticity of substitution, or isoelastic) utility
- Exponential utility
- Quasilinear utility
- Homothetic preferences
Most utility functions used in modeling or theory are well-behaved. They are usually monotonic, quasi-concave, continuous and globally non-satiated. However, it is possible for preferences not to be representable by a utility function. An example is lexicographic preferences which are not continuous and cannot be represented by a continuous utility function.[2]
Expected utility
The expected utility theory deals with the analysis of choices among risky projects with (possibly multidimensional) outcomes.
The expected utility model was first proposed by Nicholas Bernoulli in 1713 and solved by Daniel Bernoulli in 1738 as the St. Petersburg paradox. Bernoulli argued that the paradox could be resolved if decisionmakers displayed risk aversion and argued for a logarithmic cardinal utility function.
The first important use of the expected utility theory was that of John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern who used the assumption of expected utility maximization in their formulation of game theory.
Additive von Neumann–Morgenstern utility
In older definitions of utility, it makes sense to rank utilities, but not to add them together. A person can say that a new shirt is preferable to a baloney sandwich, but not that it is twenty times preferable to the sandwich.
The reason is that the utility of twenty sandwiches is not twenty times the utility of one sandwich, by the law of diminishing returns. So it is hard to compare the utility of the shirt with 'twenty times the utility of the sandwich'. But Von Neumann and Morgenstern suggested an unambiguous way of making a comparison like this.
Their method of comparison involves considering probabilities. If a person can choose between various randomized events (lotteries), then it is possible to additively compare the shirt and the sandwich. It is possible to compare a sandwich with probability 1, to a shirt with probability p or nothing with probability 1 − p. By adjusting p, the point at which the sandwich becomes preferable defines the ratio of the utilities of the two options.
A notation for a lottery is as follows: if options A and B have probability p and 1 − p in the lottery, write it as a linear combination:
More generally, for a lottery with many possible options:
with the sum of the p is equalling 1.
By making some reasonable assumptions about the way choices behave, von Neumann and Morgenstern showed that if an agent can choose between the lotteries, then this agent has a utility function which can be added and multiplied by real numbers, which means the utility of an arbitrary lottery can be calculated as a linear combination of the utility of its parts.
This is called the expected utility theorem. The required assumptions are four axioms about the properties of the agent's preference relation over 'simple lotteries', which are lotteries with just two options. Writing 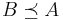 to mean 'A is preferred to B', the axioms are:
to mean 'A is preferred to B', the axioms are:
- completeness: For any two simple lotteries
 and
and 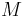 , either
, either 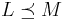 ,
, 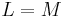 , or
, or 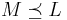 .
. - transitivity: if
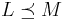 and
and 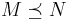 , then
, then 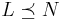 .
. - convexity/continuity (Archimedean property): If
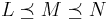 , then there is a
, then there is a 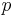 between 0 and 1 such that the lottery
between 0 and 1 such that the lottery 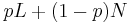 is equally preferable to
is equally preferable to 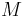 .
. - independence: if
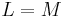 , then
, then 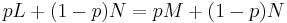 .
.
In more formal language: A von Neumann–Morgenstern utility function is a function from choices to the real numbers:
which assigns a real number to every outcome in a way that captures the agent's preferences over both simple and compound lotteries. The agent will prefer a lottery  to a lottery
to a lottery  if and only if the expected utility of
if and only if the expected utility of  is greater than the expected utility of
is greater than the expected utility of  :
:
Repeating in category language:  is a morphism between the category of preferences with uncertainty and the category of reals as an additive group.
is a morphism between the category of preferences with uncertainty and the category of reals as an additive group.
Of all the axioms, independence is the most often discarded. A variety of generalized expected utility theories have arisen, most of which drop or relax the independence axiom.
- CES (constant elasticity of substitution, or isoelastic) utility is one with constant relative risk aversion
- Exponential utility exhibits constant absolute risk aversion
Money
One of the most common uses of a utility function, especially in economics, is the utility of money. The utility function for money is a nonlinear function that is bounded and asymmetric about the origin. These properties can be derived from reasonable assumptions that are generally accepted by economists and decision theorists, especially proponents of rational choice theory. The utility function is concave in the positive region, reflecting the phenomenon of diminishing marginal utility. The boundedness reflects the fact that beyond a certain point money ceases being useful at all, as the size of any economy at any point in time is itself bounded. The asymmetry about the origin reflects the fact that gaining and losing money can have radically different implications both for individuals and businesses. The nonlinearity of the utility function for money has profound implications in decision making processes: in situations where outcomes of choices influence utility through gains or losses of money, which are the norm in most business settings, the optimal choice for a given decision depends on the possible outcomes of all other decisions in the same time-period.[3]
Discussion and criticism
Cambridge economist Joan Robinson famously criticized utility of being a circular concept: "Utility is the quality in commodities that makes individuals want to buy them, and the fact that individuals want to buy commodities shows that they have utility" (Robinson 1962: 48)[4]
Different value systems have different perspectives on the use of utility in making moral judgments. For example, Marxists, Kantians, and certain libertarians (such as Nozick) all believe utility to be irrelevant as a moral or at least not as important as other factors such as natural rights, law, conscience and/or religious doctrine. It is debatable whether any of these can be adequately represented in a system that uses a utility model.
Another criticism comes from the assertion that neither cardinal nor ordinary utility are empirically observable in the real world. In case of cardinal utility it is impossible to measure the level of satisfaction "quantitatively" when someone consumes/purchases an apple. In case of ordinal utility, it is impossible to determine what choices were made when someone purchases, for example, an orange. Any act would involve preference over infinite possibility of a set choices such as (apple, orange juice, other vegetable, vitamin C tablets, exercise, not purchasing, etc). [1][2][3]
References and additional reading
- ↑ Alfred Marshall. 1920. Principles of Economics. An introductory Volume. 8th edition. London: Macmillan.
- ↑ Jonathan E. Ingersoll, Jr. Theory of Financial Decision Making. Rowman and Littlefield, 1987. p. 21
- ↑ J.O. Berger, Statistical Decision Theory and Bayesian Analysis. Springer-Verlag 2nd ed. (1985) ch. 2. (ISBN 3540960988)
- ↑ Joan Robinson, 1962. Economic Philosophy. Harmondsworth, Middlesex, UK: Penguin Books Ltd.
- Neumann, John von and Morgenstern, Oskar Theory of Games and Economic Behavior. Princeton, NJ. Princeton University Press. 1944 sec.ed. 1947
- Nash Jr., John F. The Bargaining Problem. Econometrica 18:155 1950
- Anand, Paul. Foundations of Rational Choice Under Risk Oxford, Oxford University Press. 1993 reprinted 1995, 2002
- Kreps, David M. Notes on the Theory of Choice. Boulder, CO. Westview Press. 1988
- Fishburn, Peter C. Utility Theory for Decision Making. Huntington, NY. Robert E. Krieger Publishing Co. 1970. ISBN 978-0471260608
- Plous, S. The Psychology of Judgement and Decision Making New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993